Navigating the Investment Landscape: Key Differences Between Developed and Emerging Markets Investments

As an investor, understanding the nuances of different markets is crucial for making informed decisions about your investment portfolio. Developed and emerging markets are two distinct categories that offer varying opportunities and risks. In this article, we’ll delve into the key differences between these two markets, exploring the characteristics, benefits, and challenges of each. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, this guide will help you navigate the investment landscape and make informed decisions about your financial future.
What are Developed Markets?
Developed markets, also known as mature markets, refer to economies that are well-established, stable, and have a high standard of living. These markets are typically characterized by:
- Strong institutions and regulatory frameworks
- High-income economies
- Low inflation rates
- Developed infrastructure
- High levels of transparency and accountability
Examples of developed markets include the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Japan, and Australia. These markets are often considered lower-risk and offer relatively stable returns on investment.
What are Emerging Markets?
Emerging markets, on the other hand, are economies that are in the process of rapid growth and industrialization. These markets are often characterized by:
- Lower-income economies
- Higher inflation rates
- Developing infrastructure
- Less transparency and accountability
- Higher levels of risk and volatility
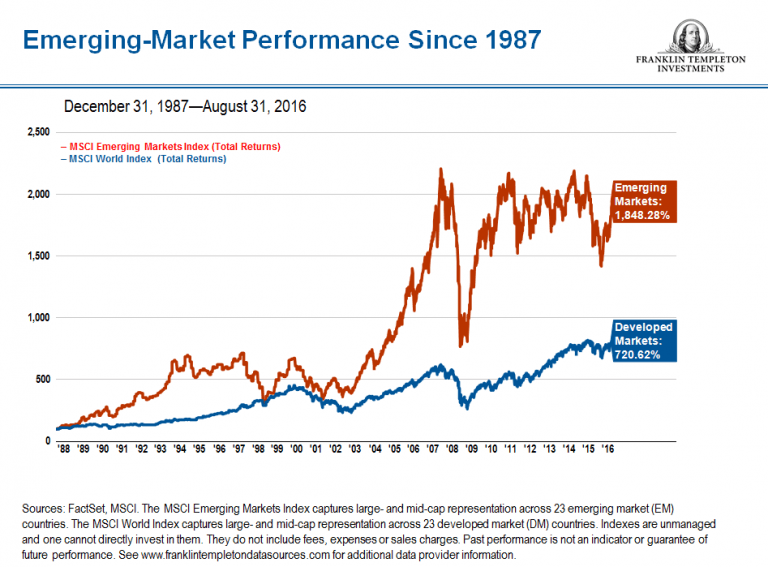
Examples of emerging markets include China, India, Brazil, Mexico, and South Africa. These markets offer higher potential returns on investment due to their growth potential, but also come with higher levels of risk.
Key Differences Between Developed and Emerging Markets
1. Risk Profile
Developed markets are generally considered lower-risk, with more stable economies, stronger institutions, and lower inflation rates. Emerging markets, on the other hand, are higher-risk, with higher inflation rates, more volatility, and less transparency and accountability.
According to a study by the World Bank, emerging markets are more prone to economic shocks, such as currency fluctuations and changes in commodity prices. This higher risk profile means that investors in emerging markets need to be more cautious and prepared for potential losses.
2. Return on Investment
Emerging markets offer higher potential returns on investment due to their growth potential. According to a study by PwC, emerging markets are expected to grow at a rate of 5-7% per annum over the next decade, compared to 2-3% for developed markets.
However, this higher return comes with higher risk. Investors in emerging markets need to be prepared for potential losses and have a longer-term perspective to ride out market fluctuations.
3. Liquidity and Accessibility
Developed markets are typically more liquid and accessible, with well-established stock exchanges, bond markets, and other financial infrastructure. Emerging markets, on the other hand, may have less developed financial infrastructure, making it more difficult for investors to enter and exit markets.
According to a report by the Financial Times, emerging markets often have lower levels of liquidity, making it more difficult for investors to buy and sell securities. This can result in higher trading costs and lower returns on investment.
4. Regulatory Environment
Developed markets have stronger regulatory frameworks, with more transparent and accountable institutions. Emerging markets, on the other hand, may have less developed regulatory frameworks, with more corruption and less transparency.
According to a report by the World Economic Forum, emerging markets often have lower levels of regulatory transparency, making it more difficult for investors to understand the risks and opportunities in these markets.
5. Investment Products
Developed markets offer a wider range of investment products, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Emerging markets, on the other hand, may have fewer investment products available, with more limited access to capital markets.
According to a report by Ernst & Young, emerging markets are increasingly developing their investment product offerings, including the growth of ETFs and other index funds. However, these markets still lag behind developed markets in terms of product diversity and availability.
Investing in Developed Markets
Investing in developed markets offers a range of benefits, including:
- Lower risk profile
- More liquid and accessible markets
- Stronger regulatory frameworks
- Wider range of investment products
However, developed markets also have some drawbacks, including:
- Lower potential returns on investment
- Higher valuations and lower yields
- More competition from established investors
Investing in Emerging Markets
Investing in emerging markets offers a range of benefits, including:
- Higher potential returns on investment
- Growth potential and increasing economic influence
- Diversification benefits for investors
However, emerging markets also have some drawbacks, including:
- Higher risk profile
- Less liquid and accessible markets
- Weaker regulatory frameworks
Conclusion
Developed and emerging markets offer different investment opportunities and risks. Developed markets are generally considered lower-risk, with more stable economies and stronger institutions. Emerging markets, on the other hand, offer higher potential returns on investment, but come with higher levels of risk and volatility.
When investing in emerging markets, it’s essential to:
- Conduct thorough research and due diligence
- Understand the local market dynamics and regulatory environment
- Diversify your portfolio to manage risk
- Have a longer-term perspective to ride out market fluctuations
In contrast, investing in developed markets offers a more stable and secure investment environment, with:
- Lower risk profile
- More liquid and accessible markets
- Stronger regulatory frameworks
Ultimately, the decision to invest in developed or emerging markets depends on your individual investment goals, risk tolerance, and financial circumstances. It’s essential to consult with a financial advisor and conduct thorough research before making any investment decisions.
Take the Next Step
Now that you understand the key differences between developed and emerging markets, it’s time to take the next step. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, we encourage you to:
- Conduct further research on the markets that interest you
- Consult with a financial advisor to discuss your investment goals and risk tolerance
- Consider diversifying your portfolio to manage risk and increase potential returns
Share Your Thoughts
We’d love to hear from you! Share this article with your friends and colleagues and start a conversation about the benefits and risks of investing in developed and emerging markets. What’s your investment strategy? Do you have a preference for developed or emerging markets? Let us know in the comments below.

